
Water-Cooled Chillers: Technology, Applications, and the Path Toward Sustainable Industrial Cooling
1. Introduction As global industrialization accelerates and climate regulations tighten, the demand for reliable, energy-efficient thermal management has surged. Among all cooling technologies, water-cooled chillers stand out for their ability to maintain precise temperatures (±0.1°C), operate quietly, and deliver high cooling capacity with lower total cost of ownership (TCO) over long duty cycles [2][4]. Widely deployed in chemical reactors, MRI machines, injection molding lines, and chip fabrication facilities, these systems...

Design, Intelligence, and Sustainable Application of Air-Cooled Screw Chillers in Modern Industrial and Commercial HVAC Systems Abstract
1. Introduction As urbanization accelerates and climate resilience becomes paramount, efficient, water-free cooling technologies are gaining strategic importance. The air-cooled screw chiller—which rejects heat directly to ambient air via finned-tube condensers—offers a compelling alternative to water-cooled systems, especially in regions facing water scarcity, high water treatment costs, or limited installation space [7][9]. Unlike centralized chilled water plants requiring cooling towers, pumps, and extensive piping, air-cooled units are self-contained, factory-assembled, and...

Advanced Design, Energy Efficiency, and Sustainable Deployment of Water-Cooled Screw Chillers in Modern Industrial and Commercial Applications Abstract
1. Introduction As global energy consumption rises and climate regulations tighten, efficient and reliable cooling solutions are critical across sectors—from pharmaceutical manufacturing and data centers to commercial real estate and food processing. Among vapor-compression refrigeration technologies, the water-cooled screw chiller stands out for its robustness, scalability, and superior part-load performance. Unlike air-cooled alternatives that reject heat directly to ambient air, water-cooled chillers use a closed-loop cooling tower system, enabling lower...
Performance, Design, and Sustainability of Water-Cooled Chillers in Modern Industrial and Commercial Applications
1. Introduction As global energy consumption in HVAC&R (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration) systems continues to rise, the demand for high-efficiency, reliable, and environmentally responsible cooling technologies has intensified. Among available options, water-cooled chillers stand out for their ability to deliver large cooling capacities (typically 100 kW to several megawatts) with exceptional energy efficiency, especially in hot and humid climates where air-cooled systems suffer performance degradation [2][7]. Unlike air-cooled...
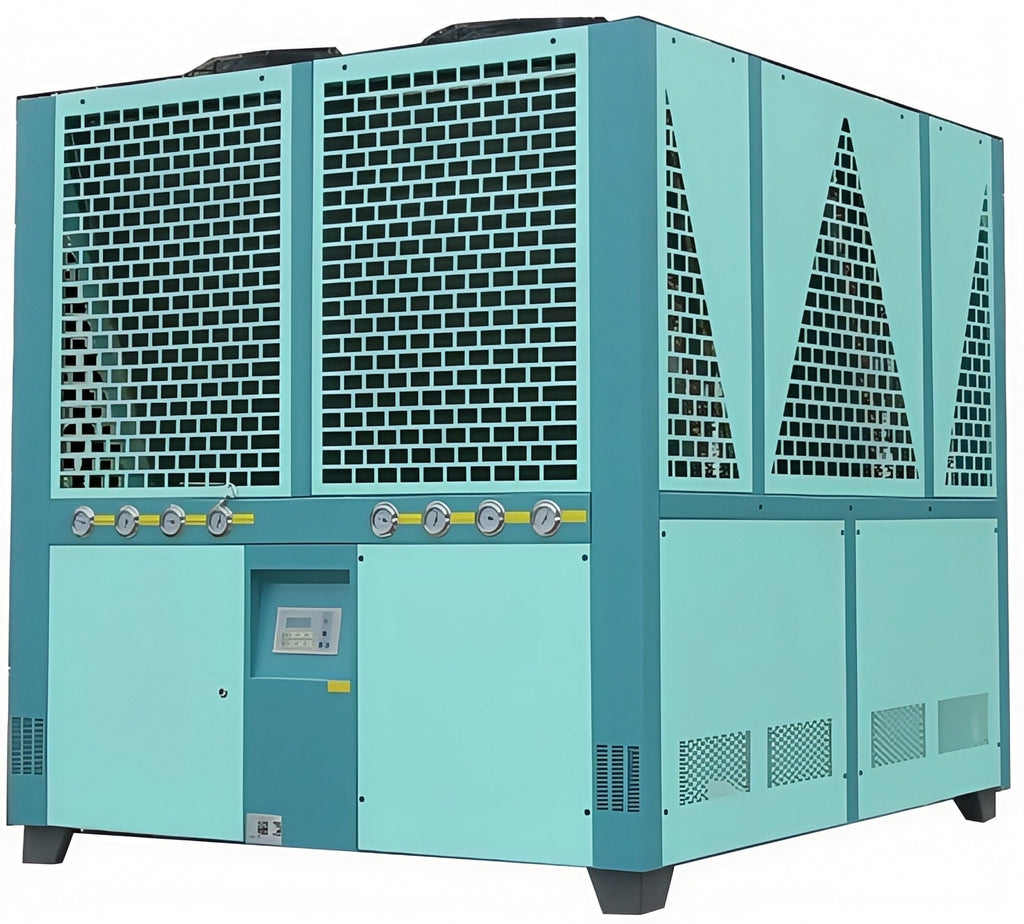

Advancements in Air-Cooled Chiller Technology: Design, Applications, and Sustainability in Modern Industrial Cooling
1. Introduction With global industrial energy consumption rising and water resources becoming increasingly constrained, the demand for efficient, low-maintenance, and environmentally responsible cooling solutions has intensified. Air-cooled chillers—also known as air-cooled industrial chillers or air-cooled box-type chillers—offer a compelling alternative to traditional water-cooled systems by eliminating the need for cooling towers, water treatment, and complex piping networks [2][5]. Widely deployed in plastics processing, laser equipment, data centers, pharmaceuticals, food &...
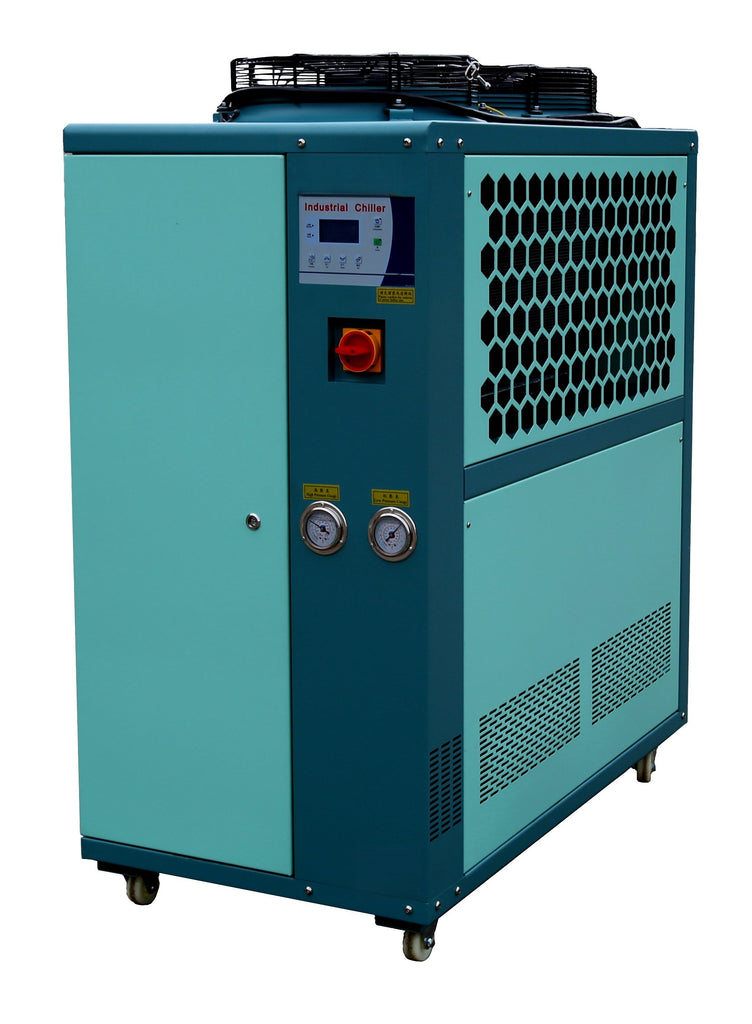

Air-cooled chiller
1. Introduction Temperature control is a critical factor in ensuring product quality, equipment longevity, and process efficiency across diverse industrial sectors—from plastics molding and laser processing to pharmaceuticals and electronics manufacturing. Among the available cooling technologies, air-cooled chillers offer a self-contained, water-free alternative that balances performance, ease of installation, and maintenance simplicity. With increasing emphasis on modular design and rapid deployment, air-cooled systems have gained significant traction, particularly in regions...
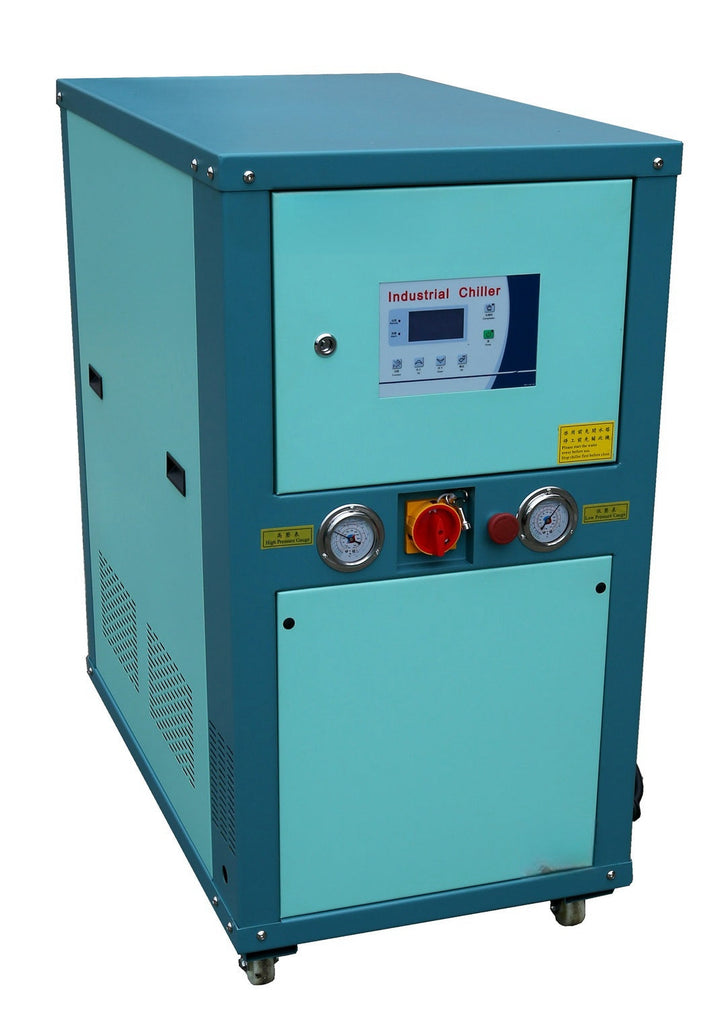

Industrial Water-Cooled Chillers: Engineering Precision for Thermal Management in Modern Manufacturing Abstract
1. Introduction: The Imperative of Process Cooling In modern industrial operations—from injection molding and laser cutting to chemical reactors and data centers—maintaining precise temperature control is not merely a preference but a necessity. Thermal fluctuations can lead to product defects, equipment failure, reduced throughput, and safety hazards. Industrial chillers serve as the central nervous system for thermal regulation, and among them, water-cooled variants are preferred for large-scale, continuous, and high-heat-load...





