1L Extrusion Blow Molding Machine: Technical Innovations and Industrial Applications
1. Introduction
Blow molding technology has revolutionized the production of hollow plastic products, offering cost-effective and scalable solutions for industries requiring lightweight, durable containers. The 1L extrusion blow molding machine specializes in producing compact containers, such as water bottles, medicine bottles, and small industrial drums. With the global blow molding market projected to grow at a CAGR of 8–10% by 2026, the 1L machine plays a pivotal role in meeting demands for precision, energy efficiency, and sustainability. This paper focuses on:
- Technical principles and design of 1L extrusion blow molding machines.
- Applications in packaging, healthcare, and industrial sectors.
- Industry trends, including smart automation and eco-friendly materials.
2. Technical Principles of 1L Extrusion Blow Molding Machines
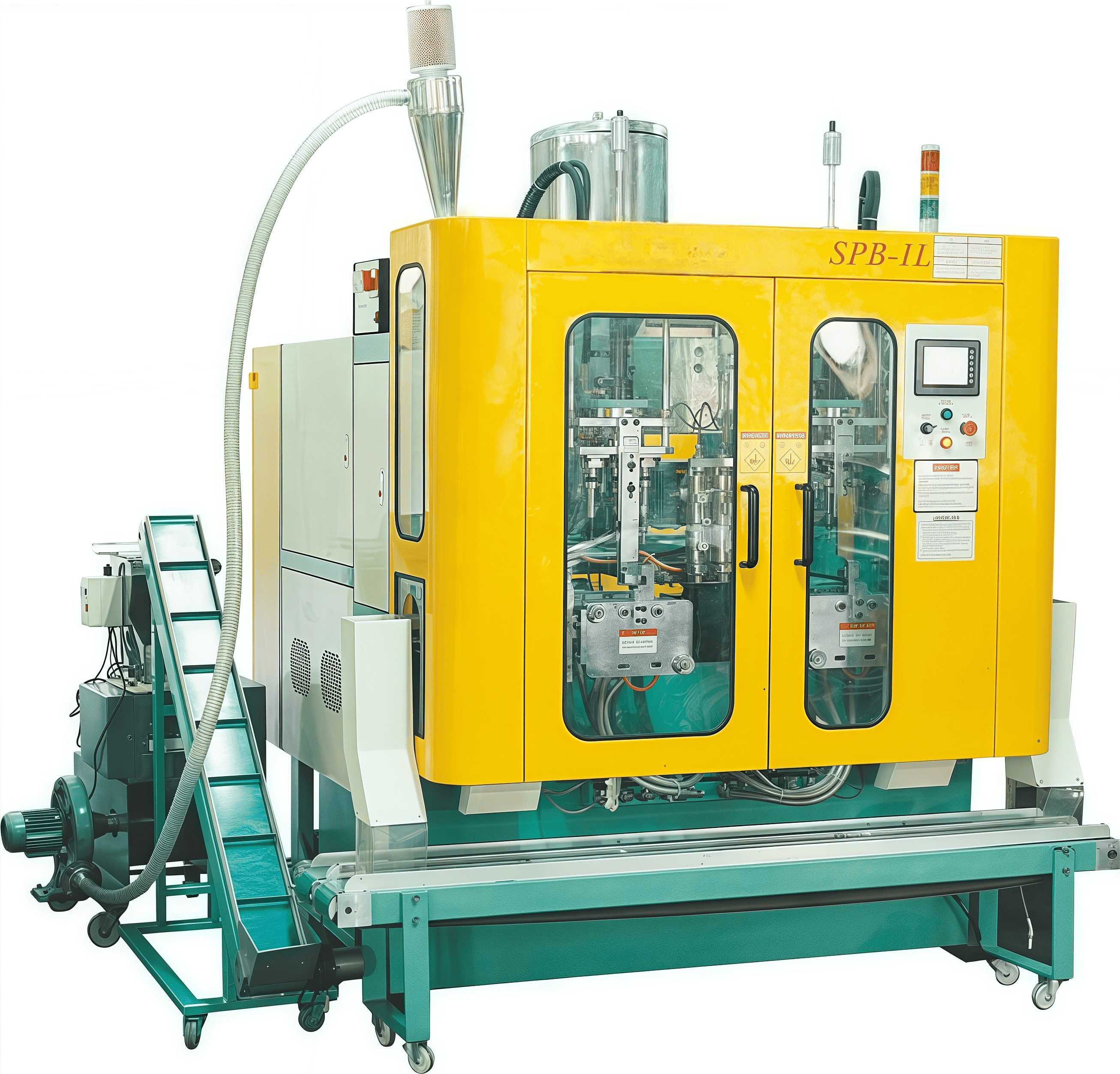
2.1 Core Components
The 1L extrusion blow molding machine consists of the following key components:
-
Extruder System:
- Converts raw plastic pellets (e.g., HDPE, PP, PETG) into a molten parison.
- Key parameters: Screw diameter (55 mm), L/D ratio (20:1), and plasticizing capacity (50 kg/h for ECM-1L2JUWD) [1].
-
Mold System:
- Dual-station design (e.g., ECM-1L2JUWD model) enables simultaneous mold opening/closing and parison extrusion.
- Center-fed die head ensures uniform thickness (reducing ovality by 50%) [3].
-
Hydraulic System:
- High-precision proportional valves control mold clamping force (50 kN for ECM-1L2JUWD) and parison wall thickness.
-
Control System:
- PLC + touchscreen interface for temperature control (±0.5°C) and process automation [6].
2.2 Working Cycle
The 1L machine follows a four-stage process:
- Extrusion: Molten plastic is extruded into a parison.
- Clamping: The parison is placed into a mold cavity (max volume: 1L).
- Blowing: Compressed air (0.8 MPa) expands the parison to match the mold shape.
- Cooling and Ejection: Rapid cooling (via water or air) ensures dimensional stability before ejection.
3. Applications of 1L Extrusion Blow Molding Machines
3.1 Beverage and Food Packaging
- Products: 1L water bottles, juice jugs, and edible oil containers.
-
Advantages:
- High hygiene standards (e.g., FDA-approved HDPE).
- Cost-effective for high-volume production (cycle time <15 seconds) [1].
3.2 Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices
- Products: Medicine bottles, IV fluid containers, and sterile packaging.
- Material Compatibility: PP’s chemical resistance and sterilization compatibility.
3.3 Industrial and Daily Chemicals
- Products: Small lubricant bottles, detergent bottles, and solvent containers.
- Precision Requirements: Wall thickness tolerance ±0.05 mm (achieved via servo-driven molds) [3].
3.4 Case Study: ECM-1L2JUWD Model in Beverage Packaging
The ECM-1L2JUWD dual-station machine (EcoMold Machinery Co., Ltd.) is widely used in China for producing 1L mineral water bottles:
- Efficiency: 50 kg/h HDPE output, 5.2-ton machine weight.
- Quality: Uniform wall thickness, smooth surface finish (99.8% defect-free rate) [1].
4. Industry Trends and Optimization Strategies
4.1 Smart Automation
- IoT Integration: Real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and cycle time via sensors.
- Predictive Maintenance: Reduces downtime by 20% through AI-driven fault detection [5].
4.2 Energy Efficiency
- Electromagnetic Heating: Saves 40–60% energy compared to resistance coils [10].
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Adjust motor speed to match production load, cutting energy use by 25% [10].
4.3 Sustainable Materials
- Biodegradable Polymers: Development of 1L containers using PLA or PBAT to meet global eco-regulations.
- Recycling Compatibility: Designing molds for easy disassembly and material recovery [11].
4.4 Multi-Layer Blow Molding
- Barrier Properties: Three-layer co-extrusion technology reduces oxygen permeability by 35% for food packaging [3].
5. Challenges and Future Directions
5.1 Technical Challenges
- Thickness Uniformity: Complex mold geometries may cause uneven parison distribution.
- Noise Reduction: Hydraulic systems generate >70 dB(A) noise, requiring acoustic shielding [3].
5.2 Future Innovations
- Hybrid Systems: Combining blow molding with 3D printing for rapid prototyping.
- AI-Driven Process Optimization: Machine learning models to predict optimal blowing pressure and cooling time.
6. Conclusion
The 1L extrusion blow molding machine is a cornerstone of modern plastic manufacturing, balancing efficiency, precision, and scalability. By adopting smart automation, energy-saving technologies, and sustainable materials, manufacturers can align with global trends toward greener and more intelligent production. Future advancements in multi-layer co-extrusion and AI integration will further solidify its role in industries ranging from packaging to healthcare.





