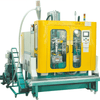
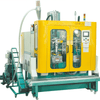
Design and Application of 1L Extrusion Blow Molding Machines in Daily Chemical Packaging Production Abstract
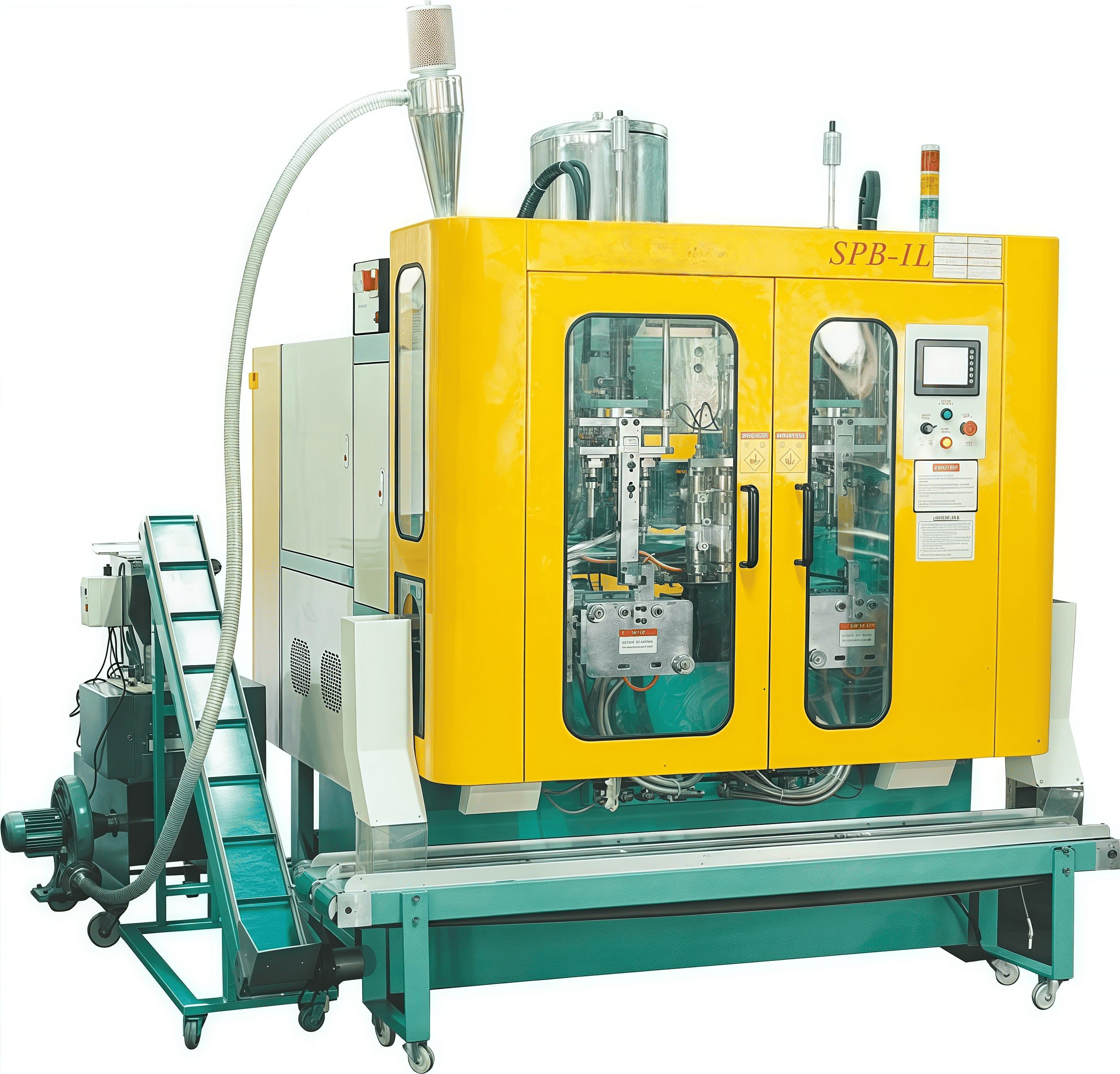
1. Introduction
The global demand for 1-liter plastic containers—particularly in the home care and personal hygiene sectors—has surged due to urbanization, e-commerce logistics, and consumer preference for standardized, easy-to-handle volumes [3][4]. In response, the 1L extrusion blow molding machine has evolved from a basic semi-automatic unit into a digitally controlled, energy-conscious production system tailored for high-mix, low-to-medium volume manufacturing.
Unlike large-scale accumulator-head machines used for IBC tanks or automotive fuel reservoirs, the 1L EBM machine prioritizes flexibility, rapid setup, and operational simplicity while maintaining wall thickness consistency (±0.1 mm) and surface finish quality [2][5]. With prices ranging from USD 14,000 to 33,000 (RMB 95,000–225,000), these machines are especially popular among SMEs in Asia, Africa, and Latin America [2][9].
This paper examines the design principles, key subsystems, and industrial applications of modern 1L EBM machines, with reference to actual product specifications from leading Chinese manufacturers such as Dongguang Jinchengxin and Cangzhou Jucheng.
2. Machine Architecture and Core Components
A typical 1L extrusion blow molding machine consists of four integrated modules:
2.1 Extrusion System
- Single-screw extruder with L/D ratio of 25:1 (e.g., Φ65 mm screw diameter) ensures uniform melting of HDPE, PP, or recycled PE at 180–220°C [2][9].
- Screw material: 38CrMoAlA alloy steel, nitrided to ≥60 μm hardness for wear and corrosion resistance [9].
- Heating power: 15 kW, often enhanced with aluminum-clad fans and intelligent temperature controllers using fuzzy PID algorithms to minimize thermal lag [12].
2.2 Parison Formation and Die Head
- Annular die head with streamlined, dead-end-free flow channels enables fast color changes and reduces melt degradation [5].
- Optional core-shell or spiral mandrel design supports 2–3 layer co-extrusion for barrier or aesthetic purposes (e.g., white outer layer + colored inner layer) [5].
- All internal surfaces are chrome-plated to ensure smooth parison extrusion and prevent material sticking [9].
2.3 Mold Clamping and Actuation
- Hydraulic or hybrid servo-hydraulic system provides clamping force sufficient for 1L molds (typically 430 mm max opening stroke, 130 mm min closing distance) [2].
- Some advanced models use a dual-driving servo motor that controls both mold opening/closing and horizontal movement on linear guides, improving positioning accuracy and reducing energy loss [1].
- Mold frames are often modular, allowing quick swap between 1-cavity and 2-cavity configurations [2].
2.4 Control and Automation
- PLC + HMI touch screen interface supports multilingual operation (Chinese/English), recipe storage, and real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and cycle time [9].
- Proximity sensors and imported limit switches enhance safety and repeatability [9].
- Optional integration with IoT platforms enables remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance—a trend highlighted in China’s 2025 smart manufacturing guidelines [4][8].
3. Process Parameters and Performance Metrics
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Output capacity | 300–600 pcs/hour |
| Material | HDPE, PP, LDPE, PCR-PE |
| Wall thickness | 1.5–2.5 mm (adjustable via parison programming) |
| Cycle time | 6–12 seconds |
| Air pressure | 0.5–0.7 MPa |
| Motor power | 11–18.5 kW |
| Machine weight | ~2,500 kg |
| Footprint | 3.0 × 1.8 × 2.1 m |
Wall thickness distribution is primarily controlled axially through manual or motorized mandrel adjustment. While full 128-point electronic profiling is rare in this class, some models (e.g., XL65-5L) offer asynchronous motor-driven parison programming that continuously adjusts die gap during extrusion to achieve targeted thickness profiles [1][5].
4. Applications in Daily Chemical Packaging
The 1L EBM machine dominates production of:
- Laundry detergent bottles (HDPE, opaque white or blue),
- Shampoo and conditioner containers (PP with glossy finish),
- Hand soap and dishwashing liquid bottles (often with integrated handles),
- Disinfectant and cleaning solution packs (requiring chemical resistance).
These products typically require:
- Smooth external surfaces for labeling,
- Uniform wall thickness to prevent collapse during shipping,
- Compatibility with post-consumer recycled (PCR) content—now mandated at ≥30% in several Chinese provinces under circular economy policies [4][8].
Notably, manufacturers like Jinchengxin offer “visible fill-line” mold inserts, allowing precise liquid-level marking without secondary printing [5].
5. Market Context and Technological Trends
According to the 2025–2030 China Extrusion Blow Molding Machine Market Report, the segment for 1–5L machines accounts for over 40% of domestic sales volume, driven by:
- Growth in e-commerce private-label brands,
- Replacement of glass and metal packaging with lightweight plastics,
- Government incentives for energy-efficient machinery (Euromap 46.1 compliance) [3][4].
Chinese OEMs have achieved significant import substitution in this tier, offering machines at 30–50% lower cost than European equivalents while meeting CE safety standards [4][8]. Brands like Jwell, Jucheng, and Jinchengxin now export widely to Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and West Africa [2][9].
Key innovation trends include:
- All-electric actuation to eliminate hydraulic oil and reduce noise (<75 dB),
- Multi-cavity molds (up to 4 cavities) for higher throughput,
- AI-assisted parameter tuning based on material batch data [4][8].
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Modern 1L EBM machines incorporate several green features:
- Variable-frequency drives (VFDs) on main motors reduce idle power consumption by 20–30% [9],
- Thermal insulation on barrel zones minimizes heat loss,
- Closed-loop cooling systems cut water usage,
- Compatibility with 100% PCR resins, supporting brand owners’ net-zero commitments [4][5].
Under China’s “dual carbon” strategy, new machines must demonstrate ≥25% energy savings compared to 2020 baselines—a target many 1L models now exceed [4].
7. Conclusion
The 1-liter extrusion blow molding machine exemplifies how mid-tier plastic processing equipment can achieve a powerful balance of affordability, reliability, and technological sophistication. Through innovations in screw design, die head engineering, digital control, and energy management, today’s 1L EBM systems deliver consistent quality for high-volume consumer packaging while aligning with global sustainability imperatives. As circular economy regulations tighten and digital manufacturing advances, this equipment class will continue to serve as a vital enabler for agile, eco-conscious plastic producers worldwide.
-
Posted in
extrusion blow molding machine